Title: Does Coronavirus Affect Teeth and Gums? Exploring the Potential Oral Health Implications
Introduction
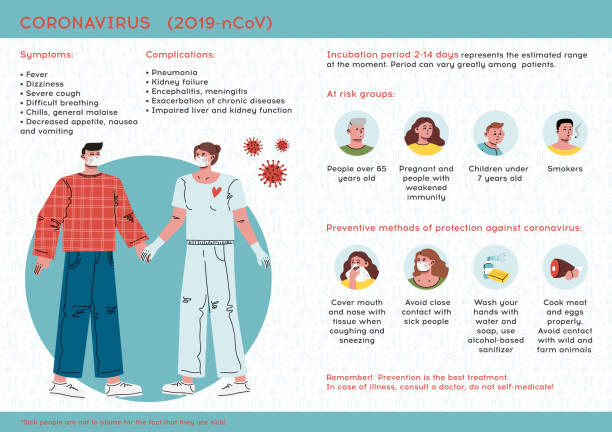
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has swept across the globe, affecting millions of lives in profound ways. While the primary symptoms of COVID-19 are often associated with respiratory distress, such as cough, fever, and shortness of breath, research is now uncovering a potential link between the virus and oral health. In this article, we delve into the emerging evidence regarding the impact of COVID-19 on teeth and gums, exploring the potential implications and offering insights into maintaining oral health during these uncertain times.
The Mouth-Body Connection
Before diving into the possible effects of COVID-19 on oral health, it's crucial to understand the mouth-body connection. The mouth serves as a gateway to the body, and its health is intricately linked to overall well-being. Numerous studies have established connections between oral health and conditions like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections. This relationship highlights the importance of maintaining optimal oral hygiene and seeking dental care, especially during a pandemic that affects the respiratory system.
Potential Oral Symptoms of COVID-19
While the hallmark symptoms of COVID-19 are centered around the respiratory system, there have been reports of various oral manifestations in individuals with the virus. These symptoms include:
Impact on Dental Care
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly disrupted routine dental care for many individuals. Lockdowns, restrictions, and fear of exposure have led to postponed dental appointments and treatments. While this was a necessary response to curb the virus's spread, it has raised concerns about long-term oral health.
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings play a pivotal role in preventing oral issues. Dental professionals not only clean teeth but also identify early signs of problems like cavities, gum disease, and oral cancers. Delayed or missed dental visits could result in undetected issues progressing to more advanced stages, potentially leading to more extensive and costly treatments in the future.
Maintaining Oral Health during the Pandemic
Amid the challenges posed by the pandemic, individuals can take proactive steps to safeguard their oral health:
Conclusion
While the primary focus of the COVID-19 pandemic has rightly been on respiratory health, emerging evidence suggests potential oral health implications. The mouth serves as a mirror reflecting the body's overall well-being, and neglecting oral health can have far-reaching consequences. As the world navigates these challenging times, individuals should remain vigilant about their oral hygiene practices and prioritize regular dental care. By staying informed and taking proactive measures, we can mitigate the potential oral health impacts of the virus and emerge from this pandemic with our smiles intact.
Introduction
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has swept across the globe, affecting millions of lives in profound ways. While the primary symptoms of COVID-19 are often associated with respiratory distress, such as cough, fever, and shortness of breath, research is now uncovering a potential link between the virus and oral health. In this article, we delve into the emerging evidence regarding the impact of COVID-19 on teeth and gums, exploring the potential implications and offering insights into maintaining oral health during these uncertain times.
The Mouth-Body Connection
Before diving into the possible effects of COVID-19 on oral health, it's crucial to understand the mouth-body connection. The mouth serves as a gateway to the body, and its health is intricately linked to overall well-being. Numerous studies have established connections between oral health and conditions like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections. This relationship highlights the importance of maintaining optimal oral hygiene and seeking dental care, especially during a pandemic that affects the respiratory system.
Potential Oral Symptoms of COVID-19
While the hallmark symptoms of COVID-19 are centered around the respiratory system, there have been reports of various oral manifestations in individuals with the virus. These symptoms include:
- Loss of Taste and Smell: One of the most common symptoms of COVID-19 is a sudden loss of taste and smell. This sensory impairment can indirectly affect oral health by altering one's appetite and dietary choices, potentially leading to nutritional imbalances that impact oral health.
- Oral Ulcers and Lesions: Some COVID-19 patients have presented with oral ulcers and lesions. These could be a result of the virus's impact on the oral mucosa or a secondary effect of systemic inflammation.
- Dry Mouth: COVID-19 patients, particularly those with more severe symptoms, may experience dry mouth. Reduced salivary flow can contribute to an increased risk of dental issues, as saliva plays a crucial role in protecting teeth and gums.
- Gum Inflammation: Emerging research suggests a potential link between COVID-19 and gum inflammation (gingivitis). The virus's presence in saliva and its ability to affect the vascular system might contribute to gum-related issues.
- Blood Clotting: Some severe cases of COVID-19 involve an increased risk of blood clotting. This could affect blood supply to oral tissues and potentially lead to oral complications.
Impact on Dental Care
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly disrupted routine dental care for many individuals. Lockdowns, restrictions, and fear of exposure have led to postponed dental appointments and treatments. While this was a necessary response to curb the virus's spread, it has raised concerns about long-term oral health.
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings play a pivotal role in preventing oral issues. Dental professionals not only clean teeth but also identify early signs of problems like cavities, gum disease, and oral cancers. Delayed or missed dental visits could result in undetected issues progressing to more advanced stages, potentially leading to more extensive and costly treatments in the future.
Maintaining Oral Health during the Pandemic
Amid the challenges posed by the pandemic, individuals can take proactive steps to safeguard their oral health:
- Optimal Oral Hygiene: Brushing teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily remains a fundamental practice for maintaining oral health. These actions help remove food particles, plaque, and bacteria that contribute to dental problems.
- Balanced Diet: Despite taste alterations, it's crucial to maintain a balanced diet rich in nutrients. Adequate intake of vitamins and minerals supports both oral and overall health.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps combat dry mouth and supports saliva production. Chewing sugar-free gum can also stimulate saliva flow.
- Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can worsen oral health issues. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake have numerous health benefits.
- Tele-Dentistry: As technology advances, many dental professionals are offering tele-dentistry services. These virtual consultations can provide guidance and assessments without the need for in-person visits.
- Immediate Concerns: If you experience oral symptoms such as persistent pain, bleeding, or swelling, it's important to seek dental care promptly, even during the pandemic.
Conclusion
While the primary focus of the COVID-19 pandemic has rightly been on respiratory health, emerging evidence suggests potential oral health implications. The mouth serves as a mirror reflecting the body's overall well-being, and neglecting oral health can have far-reaching consequences. As the world navigates these challenging times, individuals should remain vigilant about their oral hygiene practices and prioritize regular dental care. By staying informed and taking proactive measures, we can mitigate the potential oral health impacts of the virus and emerge from this pandemic with our smiles intact.